The B2B Buying Process - and how to influence it.
Buyer behavior has changed radically in the past 5 years; sales process unfortunately in most companies has not adapted and marketing has been slow to adapt.
I first noticed these changes 10 years ago, when buyers would come to meetings knowing more about the products and competitive approaches that I did. I began working on aligning buying and selling processes after meeting Dominic Rowsell, author of "Why Killer Products Don't Sell", on which much of this work is based.
This article is the second in a series of articles on aligning marketing and sales with buying behavior and it will be of value to sales and marketing professionals who wish to adapt their process to align with buyer behavior. Last week's article "A Guide to Aligning Marketing & Sales Engagement with Buying Process" discussed buyer behavior and how it is affected by risk.
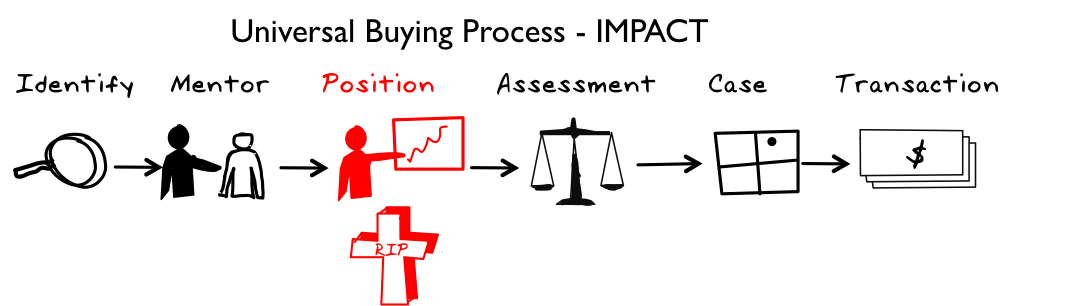
The beauty of this approach is that it's universal, simple and based on actual buyer behavior. When you understand each of the steps, you can ask buyers where they are in their buying process. Salespeople typically think that the sales opportunity is one or two steps in advance of where the buyer actually is in the buying cycle and this is a primary contributor to forecasting inaccuracy.
Phase 1: Idea or Identify
The buying process starts with an idea at Identify. 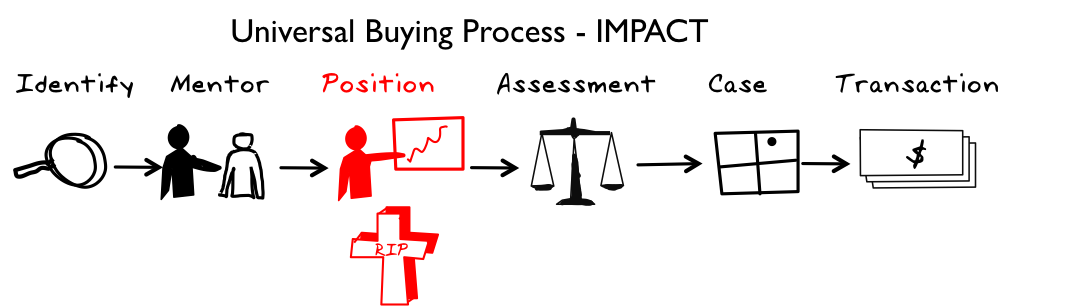
The Idea phase is usually an internal customer activity, as a result of an executive off-site meeting and blue-sky thinking, brainstorming opportunities or as a result of a strategy session. Business executives are constantly looking to identify trends in segments and markets which may yield opportunity.
A buying cycle can be initiated in answer to CXO questions like, "how can I grow revenue, expand reach, or contain cost", etc. Similarly business leaders look for economies of scale, acquisitions and to identify important customer groupings as well as emerging technologies that could help them become more competitive. Think about the last time you bought something of value...it was likely months after the idea came to you that you actually made a purchase.
Role for Marketing
Most B2B buying cycles now begin with an Internet search, but it's probably not a search for product in the first instance. Developing Mind-Share is the imperative for marketing and to get found in a Google search in response to the type of query your target buyers are using to identify possible approaches to solving the above problems.
Marketing's role is publishing fresh and engaging ideas in various forms of content in blogs, videos, article marketing, social media. Thought-leadership content takes time and intellectual-effort to create, but is worth the effort as it creates an ongoing legacy of Web pages that create brand awareness as well as providing an evergreen source of ongoing referral traffic.
Role for Sales
- Understand the Value-chain of the customer's business - this is research and may not involve customer contact.
- Engage CXO's in existing accounts in mindshare development in strategy sessions (not product related), but designed to truly understand the customer's business and to share ideas.
- Building connections with the visionaries in client organizations through social media - read their stuff, make comments on and retweet their ideas.
Risks for the Supplier
The likelihood is that salespeople will not be engaged in this phase, unless the sales team is working a multi-level strategy and senior execs are engaged at the top level of the client organization and the account team is proactive in running executive briefings.
Other risks include:
- The prospective client finds an innovative alternate approach through Google that leads to a competitor when doing "big idea" research,
- Unvalidated market analysis...this means basing your marketing plans and growth assumptions on the size of the opportunity, customer propensity to buy, the price, or any number of factors, based on incorrect assumptions. Get out of the building...read Steve Blank's HBR "Lean Startup Changes Everything"
- Lack of evidence to compare with your offering/idea....this problem is a big issue for start-ups with discontinuous technology.
- The prospect found your Website, but clicked away because they did not understand you or your offerings due to lack of clarity.
Risk Mediation
If you have a novel product/technology and you are not blogging and using social media to spread your ideas and build mind-share, you are at a distinct disadvantage, regardless of the merits of your technology.
At the outset you are not selling, you are sharing ideas on the Internet and in responding to early stage leads, you are looking to provide help and ideas in conversations of possibility.
Phase 2: Mentor
This phase is about finding and enrolling a Mentor or evangelist in the buying organization to run with/or who is already running with the idea. The Mentor is typically a senior manager or analyst who works with executive team, but is a recommender, not the decision maker.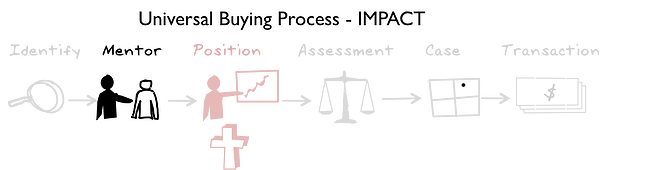
The Mentor's role is to scope and test feasibility, credibility, acceptability of the idea. The Mentor works with a small team; the idea is still under wraps and not for public consumption in the business.
- Typically will use the Internet to gather ideas and research.
- May use informal meetings with suppliers to get ideas
- Could use an RFI to gather ideas, but typically will use social networks and Google to gather ideas
The Mentor produces a report for executive team.
If accepted the Mentor will start to plan how the breakthrough idea can be implemented as an initiative, how it will be presented and to whom and the route through the political maze.
Role for Marketing
Effective Content Marketing activity generates mind-share and inbound inquiries through publishing buyer-relevant, keyword rich content and placing it where it will get found on blogs, syndicated and curated Websites and in social media specialist groups.
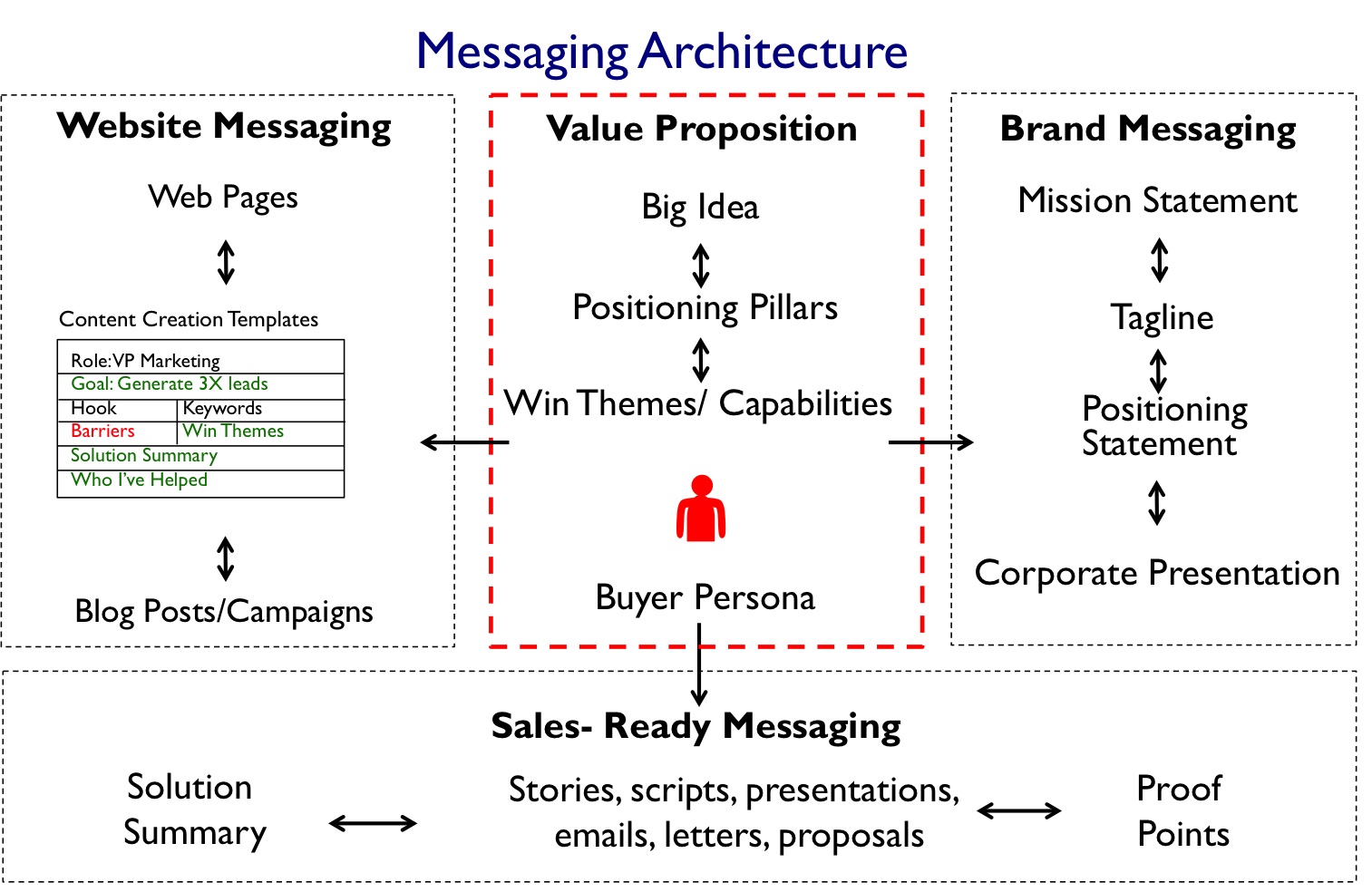
Marketing Messaging across the Buying Cycle
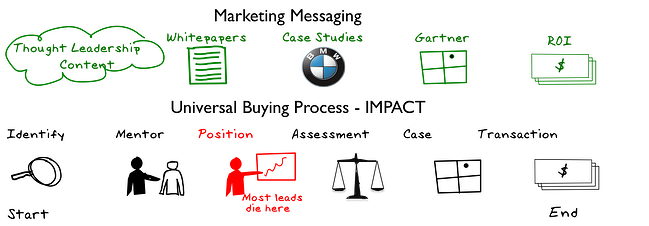
Role for Sales
The role for sales is to field these inquiries and engage the buyer in a conversation of possibilities. These are early stage inquiries from customers gathering ideas and information.
- Develop a high level engagement plan; this is not a detailed account plan or a blue-sheet; more an outline of the possible opportunity, the key players involved and the next steps for both buyer and supplier. (Mind-mapping is a perfect way of collecting and sharing high-level ideas).
- Risk analysis on customer vs. opportunity (are they the right fit, are they innovators, do they have money, can you access decision level, etc.)
This means sales managers need two green lights; one from the client that there is an opportunity for further investigation, and one from salesperson that there is indeed a worthwhile paid engagement (proof of concept, feasibility study) as a next step. - Develop conversations with prospects, - (you are not selling, you are consulting at this stage of the process). Visual confections are excellent tools for sharing big ideas, getting buyer to tell their story and getting buy-in from a wider audience in the prospective opportunity.
- If you are engaging existing accounts, sow seeds, share your ideas via hand written notes with relevant articles attached. (Emails get deleted, hand-written notes get read).
- Salespeople should try to understand buyer goals and the high level problems they are seeking to overcome.
Salespeople must identify the key players involved in the decision process; the salesperson is looking for a champion who can make things happen and to establish a relationship with that person.
Risks for the Supplier
- If the salesperson is only talking to one person in the opportunity (which is the case most of the time), and that person is a weak mentor and is not giving them access to a champion or to key decision makers on the team, then you are wasting your time.
- The customer wants you to do free work - this is a tricky call for many salespeople. As a rule in selling to the early adopter, all consulting on feasibility, product modification prototyping, etc., MUST be paid for; the supplier can refund if absolutely necessary on conclusion of a successful deal.
- Salespeople are too aggressive in trying to close a deal, instead of engaging in fully understanding the landscape of the account and the needs and goals of the key players in the decision process.
- Over-enthusiasm; the salesperson sees an opportunity and starts building expectation in the selling organization around it, without sufficient diagnosis and qualification
Now a tricky question for salespeople and their managers, What do you put in the forecast when it's still an idea on the horizon? (Answer: it does not appear on the forecast yet.)
Risk Mediation
- Salespeople need to engage powerful sponsors - politely demand it. Use the qualification confirmation letter after each meeting with a buyer. If the buyer fails to respond within a week to your meeting summary letter and confirm that your summary of the meeting is correct and follow through on next steps, (which may include access to stakeholders), they are not a prospect. This letter really works - download the template and use it.
- Identifying key players in the decision process is mandatory (also known as Stakeholder Mapping)
- If the customer is unwilling to pay for consulting on feasibility, proof of concept, or product modification, they are not a prospect.
Phase 3: Position
Public discussion occurs within the key players on the executive team to make resources and funds available. The Mentor works hard to drive the project and their own personal credibility.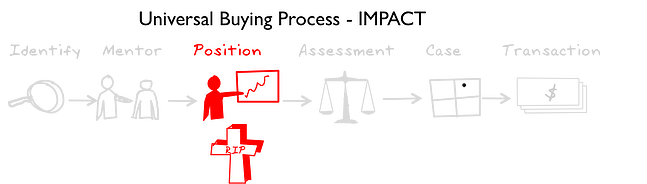
If the supplier's product is disruptive, this will arouse emotions and the positioning discussion will become POLITICAL; Change = Emotions.
Without executive sponsorship at this stage, the idea is unlikely to survive the internal battle for resources and funds.
Many potential opportunities fail to turn into projects because they are killed off at the Position phase by competing priorities or strong adversaries who are either fighting to maintain status quo, are aligned with alternate approaches, or simply don't understand your offering and by default, oppose the idea.
The transition from Position to Case is the specification for a project for the internal assessment of the idea.
Role for Marketing
After a Website visitor has converted into a lead on your Website, the process of building trust and credibility begins. Lead nurturing is the process of sending the right message to the right prospect at the right time and in most cases, this is hit and miss.
Lead nurturing is a science and it takes dedicated effort and often professional help is needed to set-up and generate meaningful results that justify the investment in the marketing automation platform.
Email is the preferred vehicle for lead nurturing, based on sending appropriate content to segmented lists of your leads, based on buyer persona role, company demographics, interest areas and sundry other criteria.
Each email should follow a logical path to educate the buyer on the issues and advantages in your approach and move them to take action. Typically top and middle of the funnel content presents an opportunity to read a new article or download a white-paper or e-book.
Role for Sales
Position is make or break time for salespeople, although few ever know when or how it occurred. Typically, (80% of the time), the buyer goes radio silent and disappears and the opportunity is over for now.
- Support your mentor and find a champion
- Generate business support for an Assessment, meet key players
- Use the meeting summary and visual confections as well as providing links to relevant examples and proof points.
- Use white papers, eBooks and presentations to circulate ideas to stakeholders.
- Understand the politics and work with the mentor/champion to develop a sequence of events to fully scope the idea.
Risks
- Strong adversaries aligned with the status-quo or alternate approaches,
- Competition for scarce resources means your idea may not survive without sufficient emotional commitment from key stakeholders,
- Behavior or process change are strongly resisted by the "USER" stakeholder of the innovation,
- Weak or no champion to fight for your solution,
- The opportunity loses momentum and client goes "radio-silent"
Risk Mediation
Any work must be a paid engagement - if the idea is worth doing, it's worth paying a little to be sure. Work the key stakeholders, understand their roles, issues - create vision as to the value of your approach.